Industrial heating: the future is Full-Electric and sustainable
In the following interview, Paolo Buzzi, Controllers & Power Controllers Marketing Manager, showcases Gefran's smart solutions to improve the performance of industrial heating systems.
What are the main trends emerging in the industrial heating industry?
The sector of industrial heating processes is embracing a paradigm shift, under the banner of sustainability. The most obvious transformation involves the transition from Gas-fired heating systems to Full-electric solutions, powered also by renewable energy sources, such as photovoltaics and wind power. In conjunction with this trend, the IEA predicts a significant increase in the use of renewable sources, driven by the need to meet the industry’s electricity needs in a more sustainable manner. Therefore, compared to the current scenario, which is still dominated by fossil fuels, a significant reversal of the trend is expected: in fact, it is estimated that in 2050, renewables will provide more than 70 percent of the electricity produced globally.
What are the challenges of this transition?
The first barrier to overcome resides in the discontinuity of “green” energy production, which mainly stems from the power fluctuations of renewable sources, such as wind and solar. By converting the current distribution network, which is characterized by a linear structure from producer to consumer, to new infrastructures with a grid configuration (where multiple consumers and producers coexist on a horizontal, and no longer hierarchical, plane), it will be possible to ensure superior delivery stability, reliability and efficiency to the system. In this regard, it is quite important for smart grids to be equipped with advanced technologies to monitor the power fed into the grid so that it is distributed effectively to all users.
A steadily growing need to access actual consumption data has also been observed at both factory and individual process levels. This will allow to create accurate forecasts according to electricity demand, creating a perfect balance between supply and demand.
On the path towards a future with zero-emissions, what are the strategies adopted by Companies?
The shared element among manufacturing companies is improving the energy performance of plants, reducing consumption and preventing inefficiencies i.e., in particular, production downtime.
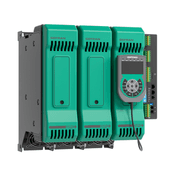
To achieve these goals, I suggest starting by identifying the type of resistive load best suited to meet the specific needs of each application. Secondly, consider using state-of-the-art Power Controllers to precisely regulate temperature during production processes, with positive effects in terms of energy savings. In this sense, Gefran’s GPC series of single-, dual- and three-phase power controllers are synonymous of maximum precision in delivering the desired power, in a wide range of contexts: from vacuum furnaces to aluminium holding furnaces, glass tempering and autoclaves for multilayer glass or composite material. Equipped with analog and digital I/Os for reporting alarm states and transmitting process variables with the most common factory communication fieldbuses, the GPCs ensure high performance within a variety of control architectures, for linear and nonlinear loads.
Finally, when used in synergy with the Smart Load Management algorithms implemented in the GSLM devices, GPC power controllers result in an innovative solution to optimize consumption by improving the energy efficiency of plants.
Can you explain how the mentioned GSLM works and what benefits it offers?
The GSLM system is designed to ensure high performance of heat treatment plants, where multiple control zones can operate at the same time. In this specific case, the solution is able to optimally manage any simultaneous power demand from the different heating zones. With GSLM, the risks linked to an inefficient power delivery management are completely removed. Specifically, the device allows to avoid peaks in power demand that can cause a dangerous grid overload, or a penalty due to exceeding contractual energy supply limits. To avoid this, Gefran’s Smart Load Manager acts like an orchestra conductor, distributing load trigger instants over time, thanks to advanced load sharing algorithms. It is also possible to set a maximum threshold of power delivered to the system (load shedding), so that it does not exceed the limits of available energy under any circumstances. Lastly, this technology facilitates the monitoring of energy KPIs, which is a key plus for optimizing the energy efficiency of the production site according to international ISO 50001 standards.
From a predictive maintenance point of view, what investments should be considered by manufacturing companies?
In the manufacturing sector, the ability to predict possible malfunctions and damaging downtime will be crucial to ensure continuity and reliability of the supply chain. In industrial heating plants, one possible issue stems from the temperature of the power terminals of power controllers.
In fact, these parts can overheat as a result of an uneven tightening or loosening during their use. These instances happen frequently and can trigger sparks or, in the most extreme cases, fires. With GPC, Gefran has chosen to equip the devices with 12 thermocouples, of which 6 are positioned at line and load terminals, allowing to constantly monitor their temperature and to find anomalies quickly in order to intervene with corrective actions of predictive maintenance, avoiding expensive production halts.
We have seen the importance of Gefran's products for the efficiency of industrial heating processes, and what are, on the other hand, the main actions taken by the Company toward the green transition?
For us, the topic of ecological transition has a twofold significance. On the one hand, through our products, we are enabling technology partners in the digital and sustainable transformation of our customers’ processes. In fact, Gefran’s signature sensors and automation components implement technologies such as Digital Twin, Condition Monitoring algorithms, and architectures for data transmission from the field to the edge and cloud, which are key to rationalizing energy consumption in factory 4.0.
On the other, as a manufacturing company, we are investing in the digitization of our processes and in the energy optimization of our production facilities. We have embarked on a decarbonization journey involving several levers and where we have involved our value chain, with the ambitious goal of neutralizing 25 percent of total emissions by 2030. In terms of energy efficiency, for example, already today 100 percent of the electricity consumed by the Group’s Italian factories comes from certified renewable sources, part of which is self-generated through photovoltaic plants.